- My Account:
- Sign In
- Register
- Make Payment
Articles.
Below are the categories for any articles that are published on our website. You can find articles on topics ranging from heating oil, propane, heating equipment, cooling, and much, much more. Our Home section also contains important tips, insightful facts and helpful how-to guides on lots of topics about everything from energy efficiency to important safety tips for taking care of your home and family. We also update our Featured Articles section with our newest and most relevant seasonal content to help you with your home services throughout the year. Check them out below...
Featured articles.
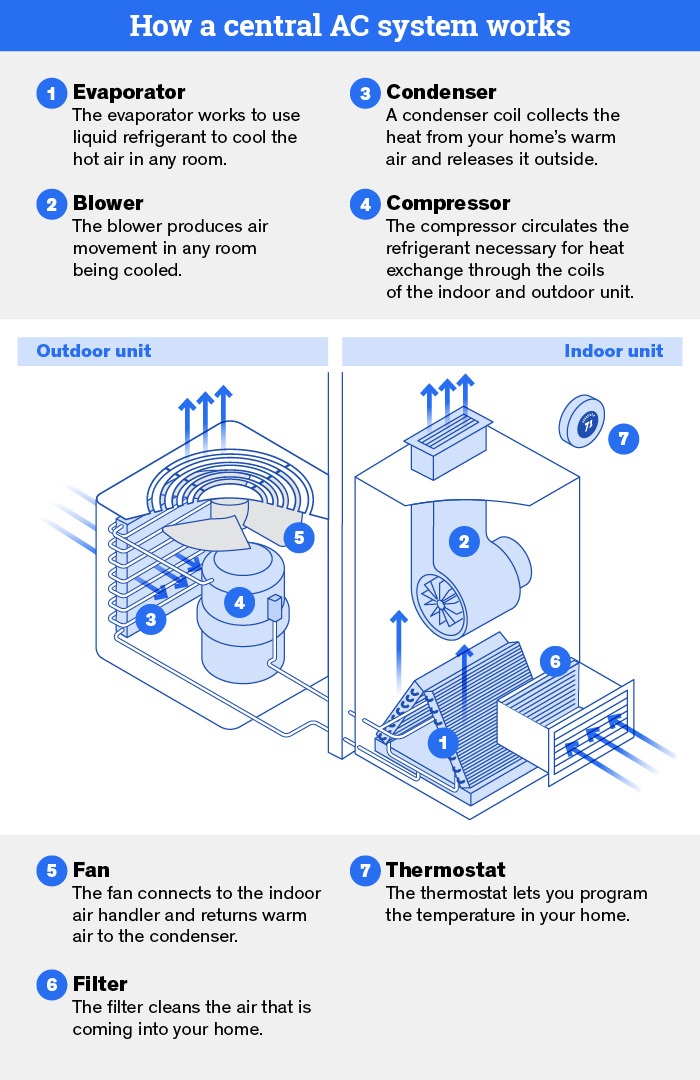
What is central AC and how does central air work?
Today, the most common form of air conditioning for homes and commercial buildings alike is central air. Central AC uses ductwork throughout a building to move cooled air from one centralized unit to multiple rooms in a building or home.
How do central air conditioning systems keep your home cool?
Central air conditioning is a type of air conditioning that allows one centralized unit to control the temperature of a building. These are common in commercial buildings and homes alike and can be used in tandem with a centralized heating unit to provide homeowners, building residents, or tenants with year-round comfort.
All central air conditioning systems consist of:
- A thermostat inside the building that controls the temperature setting. There can be multiple thermostats throughout a building, so long as each room or area has a specified duct or series of ducts.
- Ductwork that connects from the indoor cooling unit to each area that will be cooled by the unit.
- An indoor unit that converts hot, humid air from inside a building to cooler, dryer air. These are typically located in the attics of homes, as they are the hottest parts of homes and have space to house the unit without losing square footage. In commercial buildings, they are often located on the roof.
- An outdoor unit, which takes the hot air from the indoor unit and releases it into the air outside the house or building. This is connected to the indoor unit via tubing and valves.